Cells together to form tissues and tissues together to form organs. Cells are almost microscopic. Plants,fungi and bacteria etc.. have cell wall. It is the outer most covering of their cells. Cell wall is
0.2 µm thick.
Animals and man do not have cell wall. It is a non living layer. It gives shape and protection to the cell. It separates one cell to another.  |
| Cell wall |
Structure and function:

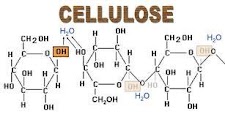
In the younger stage the cell wall is very thin, delicate and elastic this gives the cell wall the capacity to stretch . According to the age of cell wall its wall increases in its elasticity and thickness. The cell wall is formed by protoplasm . Cell wall is made up of substance called cellulose, which is carbohydrate having carbon ,hydrogen and oxygen. The cell wall consists of three layers.There are many theories about formation of cellwall.
1.The Middle lamella:
It is the outer most layer binds two adjacent cells in which wall formation is yet to be completed. It laid down first. It is rich layer in pectin.
2.The Primary cell wall:
This layer is generally thin and deposited inside the middle lamella layer. It is formed while the cells are growing. This wall is made up of carbohydrates. The major carbohydrates are cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectin. The outer most covering of Primary cell wall of plant epidermis is usually filled with cutin and wax forming permeability layer known as plant cuticle. It gives protection from water and sunlight.
3.The secondary cell wall :
The secondary cell wall layer is formed inside the primary wall after the cells are fully grown. It strengthens the cell wall because of presence of lignin. The conducting cells in xylum possesses lignin. The secondary wall contains a compounds like polymers that made up of wood. That includes cellulose, xylum and lignin. The lignin it penetrates the cell wall between cellulose hemicellulose and pectin compounds driving out water and strengthening the cell wall. The cell wall of epidermis and endodermis may also contain cutin that protects it from herbivore.
In secondary cell wall there are cavities varying in depth and depressions are called pits. Cell to cell communication is possible through pits that allow Plasmodesma. Plasmodesma are microscopic channels which traverse the cell walls of plant cell. There are two kinds of pits. Simple and bordered pits.
Bordered pits are common in the gymnospermous woods. while the simple pits are common in the angiospermous woods.
Bordered pits are common in the gymnospermous woods. while the simple pits are common in the angiospermous woods.
The cell walls in some plant tissues contain rich storage of carbohydrates. That can be used for metabolic and growth needs of plants . Plant cell wall contain structural protein and enzymes like hydrolases, esterases. In grasses , the cell wall become silicified due to the deposition of silica and this gives rigidity to the leaf blades.
Cell wall serves as a protective layer against mechanical stress. The Primary wall of the most plant cell is semipermeable and permits the passage of small molecules and proteins. Water and carbon-di- oxide is distributed throughout the plant from cellwall to cell and PH balance is controlled by the cell wall.


comments are welcome
ReplyDelete